Eustigmatophyceae is a small but important class of unicellular algae, mainly known for their high lipid content and industrial importance (biofuel, aquaculture).
General Characteristics of Eustigmatophyceae
- Mostly unicellular; rarely form simple colonies
- Cells are non-motile (flagella absent in vegetative stage)
- Found in marine as well as freshwater habitats
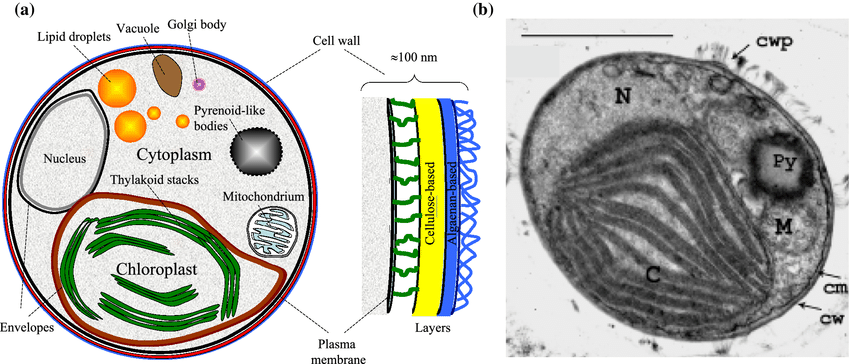
- Eukaryotic algae with a true nucleus
- Cell wall generally thick, mainly composed of cellulose
- Usually possess a single parietal chloroplast
- Chloroplast surrounded by two membranes
- Thylakoids arranged in triplets (three stacked thylakoids)
- Pyrenoids generally absent
Photosynthetic Pigments
- Chlorophyll a
- Chlorophyll c
- Carotenoids (especially violaxanthin)
- Fucoxanthin absent
- Phycobilins absent
Reserve Food Material
- Stored mainly as:
- Oil (lipids)
- Leucosin (chrysolaminarin-like polysaccharide)
- Reserve food stored in the cytoplasm
Reproduction
Mode of Reproduction
- Only asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction absent
Asexual Reproduction Methods
🔹 Vegetative Cell Division
- Occurs by mitotic division
- Parent cell divides into two daughter cells
- Each daughter cell grows independently
🔹 Autospore Formation
- Parent cell divides internally to form non-motile autospores
- Autospores are released after rupture of the parent wall
- Each autospore develops into a new individual
Life Cycle of Eustigmatophyceae
Type of Life Cycle
- Asexual
- Monogenetic
- Haploid (n)
Life Cycle Stages (Step-wise)
Vegetative Cell (n)
- Unicellular, non-motile algal cell
- Contains:
- True nucleus
- Single parietal chloroplast
- Grows under favorable conditions
Asexual Reproduction
Occurs by two methods:
(A) Binary / Mitotic Cell Division
- Nucleus divides by mitosis
- Cytoplasm divides
- Two identical haploid daughter cells formed
(B) Autospore Formation
- Parent cell divides internally
- 2–8 non-motile autospores formed
- Parent wall ruptures and releases autospores
Liberation & Growth
- Autospores or daughter cells are released
- Each develops into a new vegetative cell (n)