Skip to content
Introduction
- The nucleus is the largest membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells.
- Often called the “control center” of the cell because it stores genetic material (DNA) and regulates cellular activities.
- Typically spherical/ovoid, occupying 10–20% of cell volume.
- Discovered by Robert Brown (1831)
Structural Organization of Nucleus

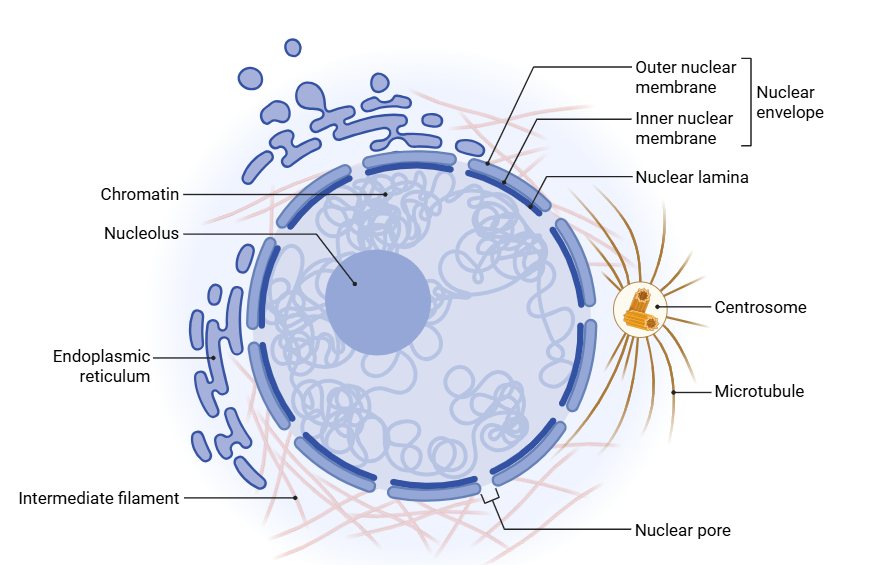
Nuclear Envelope
- Double membrane system surrounding the nucleus
- Outer membrane: continuous with rough endoplasmic reticulum, often studded with ribosomes.
- Inner membrane: lined with nuclear lamina (protein meshwork of lamin A, B, C) providing structural support.
- Nuclear pores:
- Large protein complexes (nuclear pore complexes, NPCs).
- Regulate bidirectional transport of proteins, RNAs, and ribonucleoproteins.
Nucleoplasm (Nuclear Sap)
- Gel-like matrix filling the nuclear space.
- Contains ions, nucleotides, enzymes, and soluble proteins.
- Provides medium for diffusion of small molecules and macromolecules.
Chromatin
- Complex of DNA + histone + non-histone proteins.
- Two forms (visible under light/electron microscope):
- Euchromatin: loosely packed, transcriptionally active DNA.
- Heterochromatin: highly condensed, transcriptionally inactive DNA.
- During cell division → condenses into chromosomes.
Nucleolus
- Dense, non-membranous structure within nucleus.
- Site of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis and ribosome subunit assembly.
- Contains:
- Fibrillar centers (rDNA transcription sites).
- Dense fibrillar component (processing of pre-rRNA).
- Granular component (assembly of ribosomal subunits).
Nuclear Matrix
- Insoluble fibrillar network inside nucleus.
- Provides structural framework, organizes chromatin, regulates replication and transcription.
Other Intranuclear Structures
- Cajal bodies: involved in RNA splicing and modification of snRNPs.
- Speckles: storage of splicing factors.
- PML (promyelocytic leukemia) bodies: roles in apoptosis, DNA repair, and viral defense.
Functions of Nucleus
- Genetic Information Storage
- Stores DNA in chromatin form.
- Maintains genome integrity.
- Gene Expression Regulation
- Controls transcription (DNA → RNA).
- Chromatin remodeling determines active/inactive regions.
- RNA Synthesis & Processing
- Transcribes mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, snRNA.
- RNA splicing, capping, polyadenylation occur in nucleus.
- Ribosome Biogenesis
- Nucleolus assembles rRNA + ribosomal proteins → ribosome subunits.
- Cell Division
- Chromatin condensation → chromosome segregation during mitosis and meiosis.
- Nuclear Transport
- Selective movement of molecules via nuclear pore complexes.
- Signal Integration
- Responds to cytoplasmic/nuclear signals for growth, differentiation, and stress responses.
error: Content is protected !!
